Database changes without the fear
DataVaulture makes production database changes safe and easy — with row-level previews, approval workflows, and one-click rollbacks.
Currently free — no catch. We're focused on building the best product.
DataVaulture makes production database changes safe and easy — with row-level previews, approval workflows, and one-click rollbacks.
Currently free — no catch. We're focused on building the best product.

You triple-check every UPDATE and DELETE. One typo could affect thousands of rows.
If something goes wrong, you're scrambling to restore from backup or manually fix data.
Changes go straight to production. No review process, no approval workflow.
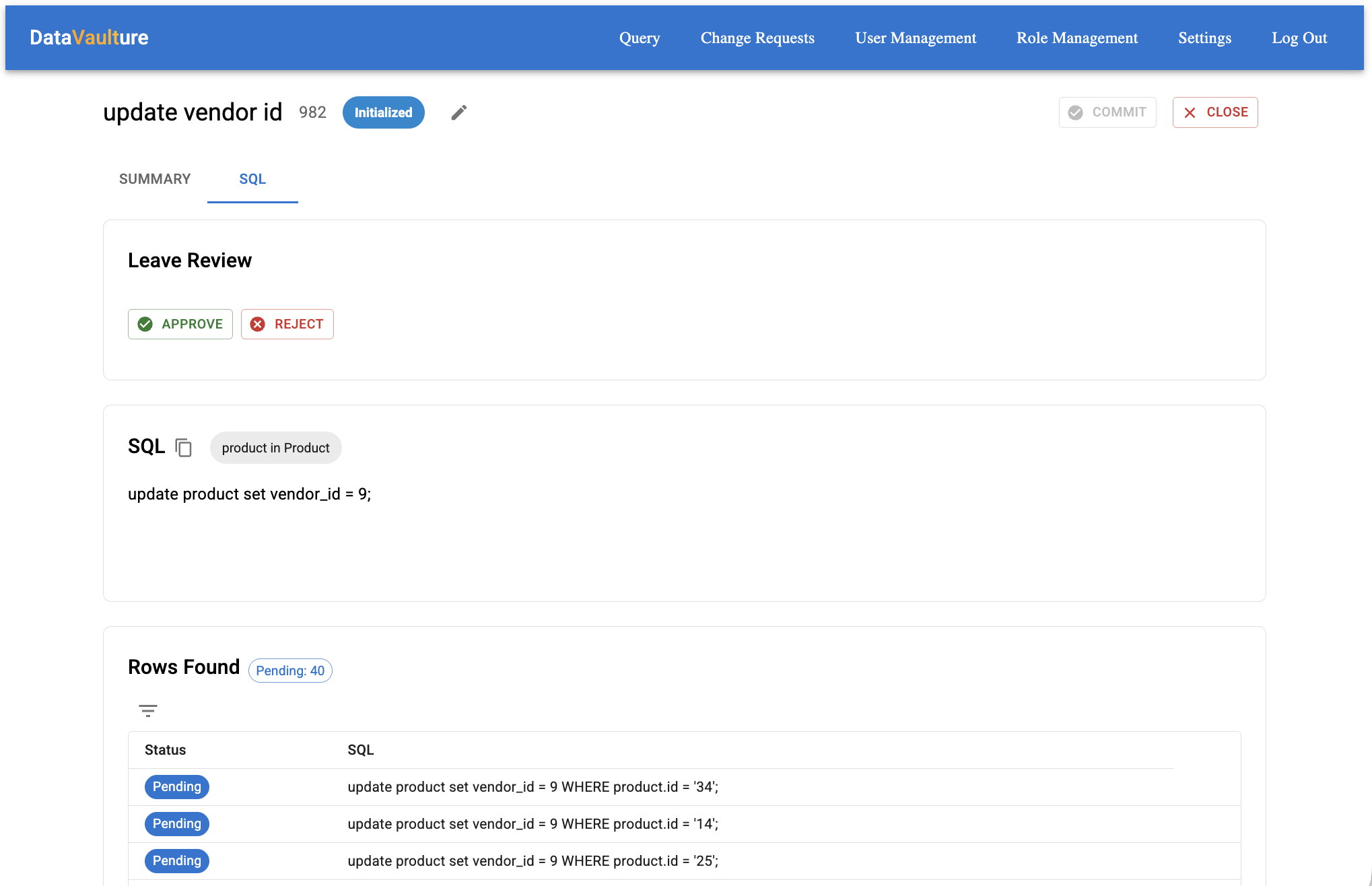
See exactly what will change before it happens. Get approvals. Roll back instantly if needed.
Write your INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. DataVaulture shows you exactly which rows will be affected.
Teammates review the change request. They see the SQL and the affected rows before approving.
Run the change. If anything goes wrong, roll back to the previous state with one click.
Watch how DataVaulture makes database management safe and easy.
DataVaulture is free to use. No credit card, no trial period, no limits.
Get Started